What is the role of dietary sugar in inflammation? Let’s dig into this major story…
Sugar and Inflammation
Who doesn’t like sweets? Most people love sweet food, especially desserts. Why not? They’re decadent and delicious, and many people find them comforting. However, too much sugar is bad for the body. Most of us know that, and more evidence supports it almost every day. They don’t call sweets “guilty pleasures” for no reason.
One adverse health effect of too much sugar in the body is its contribution to inflammation. Inflammation is part of the body’s natural defense system, wherein the body releases chemicals when exposed to tissue damages or infections. Inflammation can cause pain, swelling, and redness as it heals the injury.
How Is Sugar Linked To Inflammation?
Sugar occurs naturally in various foods, including fruits and vegetables. It’s okay to consume sugar from whole foods as nature intended, but added sugar from processed products is what brings the harmful effects. Excessive sugar in the body is harmful and damaging. Our bodies can only use relatively small amounts of glucose (sugar) in a given period.
Ingested sugar that is excess to our requirements triggers an immune response as our immune system tries to protect us from it. This defensive response includes inflammation. As excess sugar consumption is generally a habit or lifestyle component, the inflammation becomes chronic.
Here are some ways sugar can cause problems in the body that contribute to inflammation.
- Sugar Causes Unwanted Weight Gain
Sugar can give you a brief energy boost, but the effect is very short-lived. Sugar contains no nutrients. Processed foods containing large amounts of sugar don’t make you feel full, you only end up with empty calories, and too many calories can lead to weight gain.
When you gain unhealthy weight, it means you have excess body fat, which causes inflammation along with obesity.
- Sugar Leads To Plaque Build-Up In The Mouth
Bacteria in the mouth love to feed on sugar, so when you’re consuming sugar-rich foods and beverages, it can lead to plaque build-up in the mouth. That can result in tooth decay and cavities, and eventually, gum inflammation. There is a strong correlation between chronic oral inflammation and cardiovascular problems. While pain and symptoms may express themselves in localized areas, chronic inflammation is systemic and affecting the whole body.
- Sugar Increases The Gut’s Permeability
Added sugar can also increase gut permeability, which means that bacteria and toxins can more easily escape the gut lining and go the bloodstream. That will lead to inflammation in other parts of the body. It can also cause an imbalance between good and bad bacteria, resulting in inflammation associated with other digestive disorders.
- Sugar Increases Bad Cholesterol Levels
Excess refined carbs and added sugar can increase the body’s LDL cholesterol beyond safe levels, making it ‘bad’ cholesterol. Too much LDL cholesterol drives the excessive production of an inflammation marker called C-reactive protein (CRP). LDL cholesterol is one of the major factors that contribute to heart diseases and stroke.
- Sugar Leads To High Levels Of Advanced Glycation End-Products (AGEs)
Artificially sweetened food and beverages can increase the levels of AGEs in the body. They are harmful compounds that can trigger an inflammatory response and oxidative stress.
This inflammation can make your skin age faster by damaging the collagen and elastin that keep the skin firm and tight.
- Sugar Increases Insulin Resistance
Consuming too much sugar can result in chronically high levels of insulin. This results from an inability of the body’s cells to respond to insulin. The pancreas keeps trying to pump out more insulin to overcome this resistance, but this cycle is bad for your health.
It prompts an inflammatory response, which can contribute to diabetes development and heart diseases.
- Sugar Causes An Excess Fat Build-Up In The Liver
Sugar can also cause fatty liver, wherein it drives free fatty acid production in the liver. As the body breaks down these fatty acids, it can result in compounds that cause inflammation.
Large amounts of fructose can damage the liver, excess fat can build-up in the liver, and inflammation can scar the liver. Eventually, the scarring could prevent blood from getting to parts of the liver, resulting in cirrhosis.
Start Saying No to Added Sugar
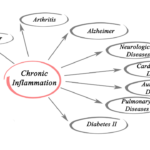
It’s very clear that too much sugar is bad for the body, and many studies have established its link to inflammation. Several chronic diseases are linked to inflammation, so it is important to start saying no to added sugar and refined carbs. Otherwise, you increase the risk of getting the following diseases:
- Heart disease
- Cancer
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Liver disease
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Arthritis
- Mental decline
Reduce your consumption of artificially sweetened food and beverages. If you’re craving sweets, it’s better to get it from fruits. Choose whole-grain carbs and eat more vegetables and antioxidant-rich food.
Managing your stress levels and staying active can also help protect your body from inflammation. Developing healthy eating habits and sticking to them can make a huge difference in having a healthy body and quality life.
Indulging in sweet treats from time to time is okay.
However, the next time you’re reaching out for that 3rd cookie or that extra slice of cake, think about the harmful effects of sugar and inflammation. At least plan ahead to have a healthier naturally sweet snack like fruit on hand to take its rightful place in your daily menu.